Journal of Bionic Engineering (2024) 21:803–820 https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-024-00484-9
A Piezoelectrically Driven Microrobot Using a Novel Monolithic Spatial Parallel Mechanism as Its Hip Joint
Guangping Wu1,2 · Ziyang Wang1,2 · Jiaxin Zhao1,2 · Feng Cui1 · Xinghan Cai1
1 National Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro and Nano Manufacture Technology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China 2 Department of Micro-Nano Electronics, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
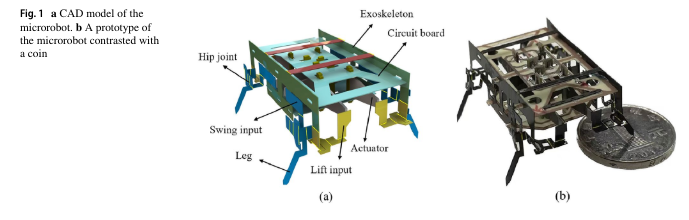
Abstract Inspired by the fast, agile movements of insects, we present a 1.9 g, 4.5 cm in length, piezoelectrically driven, quadrupedal microrobot. This microrobot uses a novel spatial parallel mechanism as its hip joint, which consists of two spatially orthogonal slider-crank linkages. This mechanism maps two inputs of two independent actuators to the decoupled swing and lift outputs of a leg, and each leg can produce the closed trajectories in the sagittal plane necessary for robot motion. Moreover, the kinematics of the transmission are analyzed, and the parameters of the fexure hinges are designed based on geometrical constraints and yield conditions. The hip joints, legs and exoskeletons are integrated into a fve-layer standard laminate for monolithic fabrication which is composed of two layers of carbon fber, two layers of acrylic adhesive and a polyimide flm. The measured output force (15.97 mN) of each leg is enough to carry half of the robot’s weight, which is necessary for the robot to move successfully. It has been proven that the robot can successfully perform forward and turning motions. Compared to the microrobot fabricated with discrete components, the monolithically fabricated microrobot is more capable of maintaining the original direction of locomotion when driven by a forward signal and has a greater speed, whose maximum speed is 25.05 cm/s.
Keywords Insect-like · Crawling microrobot · Piezoelectric drive · Parallel mechanism · Monolithic fabrication
Copyright © 2024 International Society of Bionic Engineering All Rights Reserved
吉ICP备11002416号-1









